Business Energy Keywords: Made Simple

If you’re not already familiar with the energy industry, all the terms that are thrown at you can get very confusing.
At Purely Energy we want you to understand any information we relay to you and help you as much as we possibly can. That’s why we have created a Jargon Buster for you to familiarise yourself with any terms you may not already be familiar with.
If you need help finding out who your supplier is, you can use these websites:
Alternatively, you can ring us on 0161 521 3400 or email us on Info@purelyenergy.co.uk and our team of energy experts will be happy to help.
Automatic Meter Reading (AMR):
The term describes a metering system that gives automatic meter readings remotely. This system typically uses telecommunications technology to transfer the data from the meter to a central hub, used for billing or analysis purposes. Half-hourly metering is an example of AMR technology.
Capacity Charge:
This is a fee charged by suppliers to cover investment and maintenance of the electricity network. The fee is based on agreed capacity for the site and usually only charged for sites with an availability over 100 kVa.
Change Of Tenancy (COT):
It is the process of letting your provider know you are moving out of/into a property and, hence, required to either conclude or start a new contract for your energy supply.
Climate Change Levy (CCL):
CCL is a government tax used to encourage energy efficiency for business energy users. CCL is charged as units / kWH by energy suppliers. The chargeable rate is reviewed 1st April every year, and to date has increased year on year since its introduction.
Data Aggregator (DA):
A Data Aggregator is an agent designated to aggregate the meter reading information and forward this data to your energy provider. Your DA is ordinarily the same organisation as your Data Collector, as numerous operators offer combined DCDA contracts.
Data Collector (DC):
The organisation which is responsible for deciding the amount of energy you've been provided to guarantee you are charged accurately. To do this, the DC visits your meter to take a manual read, or remotely gets the information through a secure network. Clients with half-hourly meters must designate a DC. By default, your commerce energy provider will likely act as your DC. However, companies can nominate an independent third party.
Distribution Network:
The network that carries lower voltage electricity which has been converted from the high voltage transmission network to industrial, commercial, and domestic consumers.
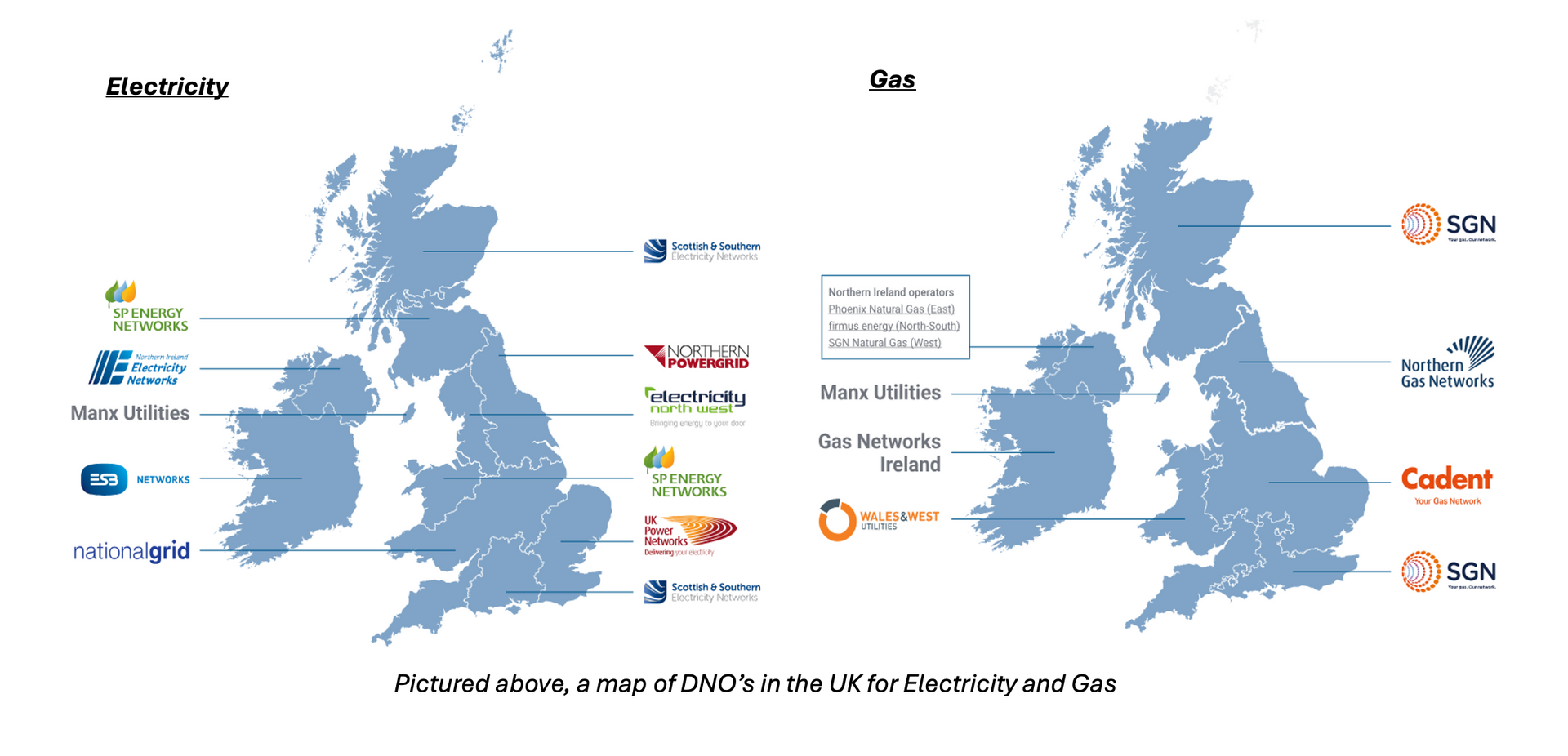
Distribution Network Operator (DNO):
A company authorised to distribute gas or electricity in the UK. These companies are responsible for the cables, towers and gas pipes that bring gas and electricity to homes and businesses.
Distribution Use of System Charges (DUoS):
These charges are the cost to deliver electricity from the grid to the customer’s site.
EAQ or EAC:
Your EAQ (Estimated Annual Quantity or Consumption) is how much, on average, electricity your house uses in kWh per year.
Energy Broker:
Energy brokers are experts in the energy industry.
Energy brokers work with businesses looking to save money on energy bills or get the right energy plan. An energy broker is a company that finds the best possible rates from energy suppliers for their commercial and industrial customers. Energy brokers typically get paid by the suppliers through the unit rates and negotiate with the suppliers to find lower energy prices.
Energy Supplier:
The business that presents you with your electricity and gas bills. Energy Suppliers buy energy in the wholesale market and sell it directly to consumers.
Fixed Rate Tariff:
Fixed Rate energy tariffs are a type of gas and electricity tariff that offer a locked-in rate per kWh for an assigned period (usually one year or more). These tariffs protect businesses from sudden energy price rises on the wholesale market.
Half-hourly Data (HHD):
The energy consumption data that is read directly from a half-hourly meter. Energy providers often analyse HHD to help them determine a customer's contract price.
Half-hourly (HH) meter:
Electricity or gas meters that read at half-hourly granularity. A half-hourly meter is a specialised type of business electricity meter that uses telecommunications technology to take and transmit meter readings every half hour.
Kilowatt (kW):
A unit of electrical power. 1 kW is proportionate to 1000 watts.
Kilowatt Hour (kWh):
A unit of gas and electricity proportionate to the energy required to run a 1,000-watt (1 kilowatt) appliance or gadget for an hour.
KVA:
A kVA is 1,000 volt-amps. It's what you get when you multiply the voltage (the force that moves electrons around a circuit) by the amps (electrical current). Kilovolt-amps measure what's called the 'apparent power' of a generator.
Letter Of Authority (LOA):
A signed letter approving another person or company to manage your energy accounts on your behalf. LOAs are commonly requested by third-parties e.g. Energy brokers, to allow them access to energy data from your Data Collector.
Maximum Demand:
Maximum demand is the highest peak of electricity usage in a half hour period, measured over a calendar month.
Maximum Demand Meter:
A maximum Demand Meter is an electricity meter usually found in businesses with mid-electricity consumption. If the meter profile (The first two numbers of an MPAN) is 05, 06, 07 or 08, then there is a maximum demand meter.
Mega Watt Hour (MWh):
One thousand kWh's.
Meter Asset Manager (MAM):
A company responsible for designing, installing, commissioning, maintaining, removing and disposing of gas supply meters. MAMs are the gas meter equivalent of an electricity meter operator (MOP).
Meter Operator (MOP):
A company that goes to a site, installs meters and provides any required ongoing meter maintenance. A MOP contract is a legal requirement for all half-hourly meters.
Metering Point Address Details (MPAD):
Information about the physical location of a meter. Also commonly known as the 'Site Address'.
Meter Point Administration Number (MPAN):
An MPAN is a 21-digit unique number utilised to distinguish electricity supply points. It is also sometimes called the 'Supply Number' or 'S Number.' You can find the MPAN on the physical electricity meter. An MPAN is commonly separated into two segments: the core and the top-line data. The core is the last 13 digits and is the unique identifier. The top-line data gives information regarding the supply's characteristics, which is the supplier's responsibility.
Meter Point Reference Number (MPRN):
A unique 6-10 digit code for a gas supply point which can be found on your gas bills. It can also be referred to as an 'M Number'.
Meter Serial Number (MSN):
A unique number that identifies a physical electricity or gas meter and can be found on the meter. If the meter is changed, your MSN will also change, but your MPAN or MPRN will stay the same.
National Grid:
All electricity and gas in the UK pass through the national grid systems. They are responsible for feeding electricity generated in the mainland UK to the distribution networks.
Non-half-hourly (NHH) meter:
Electricity or gas meters that don't read data at half-hourly granularity – usually smaller energy supplies.
Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (OFGEM):
The government regulator for the electricity and gas markets in the UK. Their job is to shield consumers by working to provide a greener and moral energy system.
OOC Rates / Deemed Rates:
This means out-of-contract rates, which are typically more expensive than a fixed tariff.
Profile Class (PC):
A meter's Profile Class provides the electricity supplier with an expectation about how electricity will be consumed by the meter throughout the day. There are eight profile classes. The first two digits of a meter's MPAN represent its Profile Class.
Renewable Energy Tariff:
A tariff where 100% of your electricity is produced from renewable resources and, often, a portion of the gas provided is 'green gas'.
Smart Meter:
Smart meters can automatically send data about your energy consumption to your energy provider, disposing of the need for you to take and submit manual meter readings. They can also display your energy use on digital displays.
Standard Variable Tariff:
An energy deal in which the rate you pay for gas and electricity fluctuates. This type of tariff is regularly more costly than a fixed-rate tariff. If you've previously had a Fixed Rate Tariff and failed to switch after it expired, you likely will have been moved to your supplier's standard variable tariff. (OOC Rates)
Standing Charge:
The rate you pay your energy supplier which will remain the same regardless of how much energy you use. The standing charge covers the upkeep of your connection to the mains supply and servicing of your account.
Sub-metering:
The process of installing meters or data loggers downstream from a main utility meter. Basically, it is a way to measure the electricity consumption of individual appliances. You can use this data to determine how much each appliance costs you. The process applies to water meters, gas meters, or electricity meters.
Transmission Network:
The network of pylons and cables that transmit higher voltage electricity from power stations where it's produced, to areas where it's required all over the UK.
Transmission Use of Systems:
The cost to transmitting electricity across the National Grid from where it was generated to the local distribution company.
Unit Rate:
The price per unit of energy in kWh that a supplier charges.
If you are struggling to understand the difference been which is better for your business, a lower unit rate or standing charge, read are article here to find out more.




